Finding the Perfect Match: How to Choose the Right Fuel Type
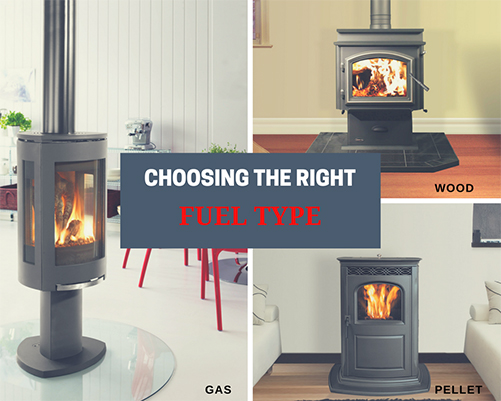

Heating a home with wood has long been the tradition here in Central Oregon. Many homeowners still use wood because it’s simply the cheapest way to heat. However, heating with wood isn’t for everyone and some homeowners may prefer the convenience of a gas stove or the efficiency of a pellet stove. So how do you know which fuel type is the right fit for you? Here at Fireside, we understand this struggle. That’s why we put together this handy reference guide. We break down the pros and cons for each fuel type to help you find the perfect match for your family, home and lifestyle.
Wood
Pro: Wood burning stoves are ideal for people that live on acreage or have access to free, locally sourced firewood. The biggest advantage or wood stoves is the quality or “warmth” of heat a unit gives off. They can produce BTUs that range from 30,000 - 120,000! Newer, EPA certified wood stoves are up to 50% more energy efficient than older models and often use 1/3 less wood. Another great advantage of heating with wood is that it works regardless of your home’s supply of gas or electricity. So in the event of a power outage, your wood stove would still heat and most work as an emergency cooking source.
Con: In most cases - folks split, haul and stack their own wood making it the most labor intensive of the three fuel types. Additional space and coverage is needed to house the bulky wood and can be an issue for people with limited storage space. Wood stoves require daily attention and can be the most challenging to regulate when it comes to heat output. They can also be messy. You’ll have to deal with debris left behind by the wood and kindling and then also removing the ash from the firebox on a regular basis. Annual maintenance from a chimney sweep is required to keep the unit functioning as properly and efficiently as possible. It’s also a safety issue in avoiding creosote build-up which can result in a chimney fire.
Bottom line: Wood stoves are ideal for people looking for the cheapest, hottest way to heat their home.
Gas
Pro: Gas stoves are the easiest of the the three fuel types to operate. With the touch of a button, gas stoves begin to work immediately. They feature a simple on/off button, a wall thermostat or a wireless remote control to operate the unit. You can also adjust the flame height, fan speed and ambient lighting. Gas stoves can heat 600 - 2000 sq/ft. and range from 14,000 - 40,000 BTUs. In the event of a power outage, newer gas stoves have battery back up systems and can run for a few weeks on four AA batteries. There is no ash to clean up and gas stoves don’t require weekly or monthly maintenance.
Con: It’s a fossil fuel and is not renewable, making it the least eco-friendly option compared to the other fuel types. Gas stoves lack the crackling sounds and aromatic firewood smell emitted from a wood burning unit. Installation of a gas unit can be more costly because it may require a gas line or propane tank to be installed, as well. The price of natural gas is pretty consistent where as liquid propane costs can fluctuate drastically. Liquid Propane units also have lower BTUs and don’t burn as clean as natural gas units.
Bottom line: Gas stoves are ideal for people who are interested in convenience and cutting the chill as opposed to getting the hottest heat output.
Pellet
Pro: Wood pellets are made of compressed sawdust so they are considered both a renewable energy source and environmentally friendly. The efficiency of an EPA certified pellet stove ranges from 70%-83%. Pellet stoves are convenient to operate because they are thermostatically controlled. A large hopper full of pellets can last all day or even longer. Pellet stoves also have blower fans to help circulate the heat and can be vented out the back of the unit cutting costs on material and providing a cleaner look. Pellet stoves have a much higher combustion and efficiency rate than wood stoves. They also create less ash than wood, making it less of a hassle to clean up. A pellet stove can range from 8,000 - 90,000 BTUs and can provide heat for a house as little as 700 sq/ft. up to 3,900 sq/ft.
Con: Pellet stoves rely on electricity and require the most maintenance out of the three options. It’s recommend that owners perform daily, weekly and monthly maintenance tasks as well as an cleaning by a chimney sweep. Pellet stoves have more components such as: multiple fans, an auger motor, an igniter and an electronic circuit board. More components can sometimes mean more parts to replace. In the event of a power outage you would need to have a back-up generator (min 1,500 watt) or inverter on hand to continue the use of your pellet stove. In order to get the best deal on pellets you need to buy in bulk (buy the ton). Which can be a disadvantage for folks with limited storage space. The flame aesthetics are considered less desirable than wood or gas stoves.
.Bottom Line: Pellet stoves are ideal for people who want the quality burn of a wood stove but with the ease and operation of a gas stove.
Ultimately, the decision is up to you. However, we hope this article helps you get a better idea of which fuel type would be the perfect match for you. So now what? Browse our stoves catalog to view a variety of styles each fuel type has to offer. Then, request a quote or stop by Fireside to talk to one of our stove experts. They will be happy to answer any of your questions and will assist you in selecting the right model for your choice of fuel type.